Note:
This post represents the synthesis of the thoughts, procedures and experiences
of others as represented in the articles read in advance (see previous posts)
and the discussion among the students and instructor during the Advanced
Analytic Techniques class at Mercyhurst University, in September 2018 regarding
IPB as an Analytic Method, specifically. This technique was evaluated based on
its overall validity, simplicity, flexibility and its ability to effectively
use unstructured data.
Description:
Intelligence
Preparation of the Battlefield (IPB) is an analytic method for understanding
the threat and environment in a specific geographic area. The military has
applied IPB to analyzing the mission variables of enemy, terrain,
weather, and civil considerations in an area of interest to determine their
effect on operations. As a result of
this process, unit leaders are able to: describe the unit’s operating
environment as well as the effects the environment has on the unit, and
determine likely courses of action (COA) by the adversary.
Strengths:
- Provides base to assess
intelligence gaps in the environment
- Helps prioritize requirements
- Increases awareness of the
battlespace
- Structure allows analysts to
identify extraneous information
- Flexible based on terrain,
operations, contingencies
Weaknesses:
- Does not take 2nd and 3rd
order effects of battle into consideration when planning
- Assumes adversary is fighting
“the same battle”; Conventional-on-Conventional warfare vs.
Conventional-on-Guerrilla warfare (i.e. Vietnam)
- Depends on analyst experience
level
- Requires understanding of
tactics and maneuvers
- Is dependent on leader
guidance and direction in requirements
- Requires knowledge of
adversary commander and forces
How-To:
- Define the battlefield
environment
- Describe the battlefield
effects
- Evaluate the threat
- Determine threat courses of
action (COA)
Application
of Technique:
Analysts
constructed a terrain model from a topographical map of Gettysburg. Sand
was used to create the terrain and depict changes in elevation. Roads were identified with black yarn and
water was identified using blue yarn. After completion of the terrain model,
key terrain within the area of operations were identified.
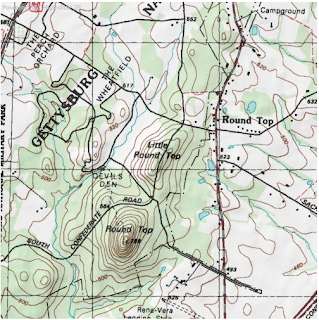 |
| Topographical Map of Gettysburg (1863) |
 |
| Application of Technique using a Sand Table to create a Terrain Model of the map shown above. |
For Further Information:
- FM 34-130:
Intelligence Preparation of the Battlefield
- Street
Smart: Intelligence Preparation of the Battlefield for Urban Operations



The market intelligence department I manage at a global manufacturer and wholesale distributor of a relatively new alternative consumer product use IPB to help develop models of total addressable market space and barriers to compete in each country. This has critical implications on go-to-market strategy and helping DMs decide which markets to invest in (sales reps, marketing, product launches, pricing, sales channels, etc).
ReplyDeleteAs an example when the company evaluated Eastern Europe, industry magazines pegged the total market size of Country A at $100 MM and Country B at $30 MM. IPB helped reduced uncertainty and helped the company decide that Country B is actually a better bet long-term due to factors such as competitive pressures (Country A has close to 1,500 physical points of sale but an industry behemoth controlled nearly 900 points of sale at the time and has since consolidated the country even further by acquiring most other shops and flooding the market with cheap products); the consumer's flavor palate; the segmentation of products by price; and more.
Have a $wagilicious day!